Retail must do the heavy lifting in realigning the marketing of Indian tea. While online transactions are more common now than in past years, neighborhood kirana stores are the most commonplace Indians purchase packaged tea, accounting for 70% of sales. Supermarkets are the fastest-growing sales channel for packaged teas. Only 7% of tea is sold at tea shops that specialize in loose-leaf offerings. Household penetration is 88% and even in rural areas 75% of households now purchase packaged tea, but on average only 22% of households report spending more than INRs200 per month on tea, according to the Tea Board of India.
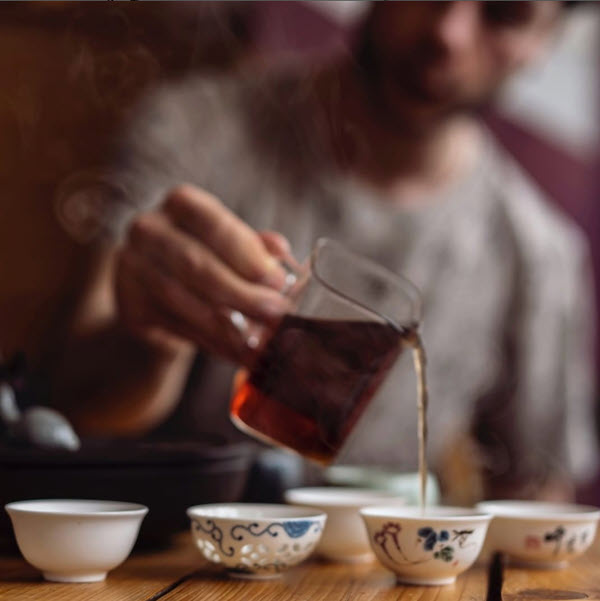
- Caption: In Delhi, Mittal Teas opened in 1954. Nikita Mittal serves a cup to her father Vikram.

Convincing Customers to Take that First Sip
By Aravinda Anantharaman
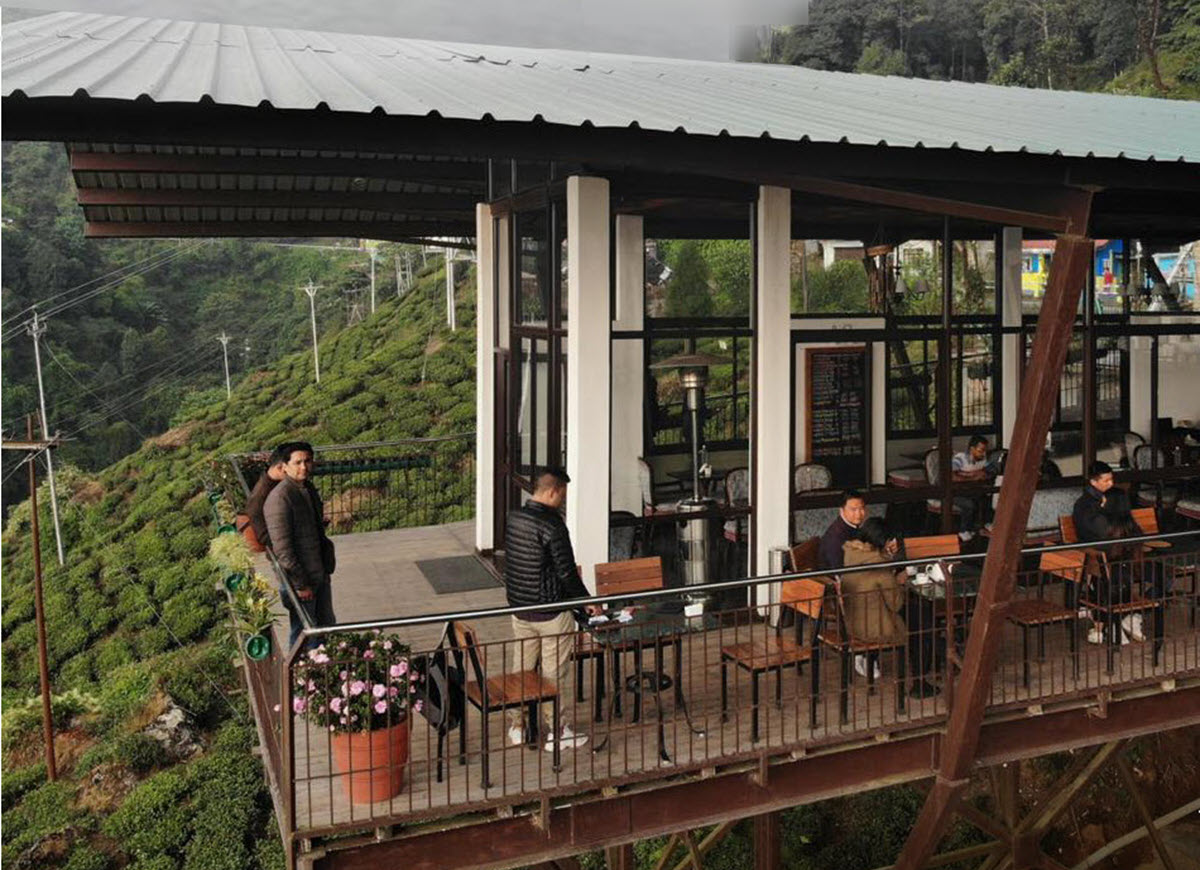
On the road between Siliguri and Darjeeling, a small tea stall would beckon visitors to stop for a break as they approach Margaret’s Hope Tea Estate. The estate ran the modest stall for years, the only convenient place for tea during the three-hour journey, says Atul Asthana, managing director Goodricke Group.
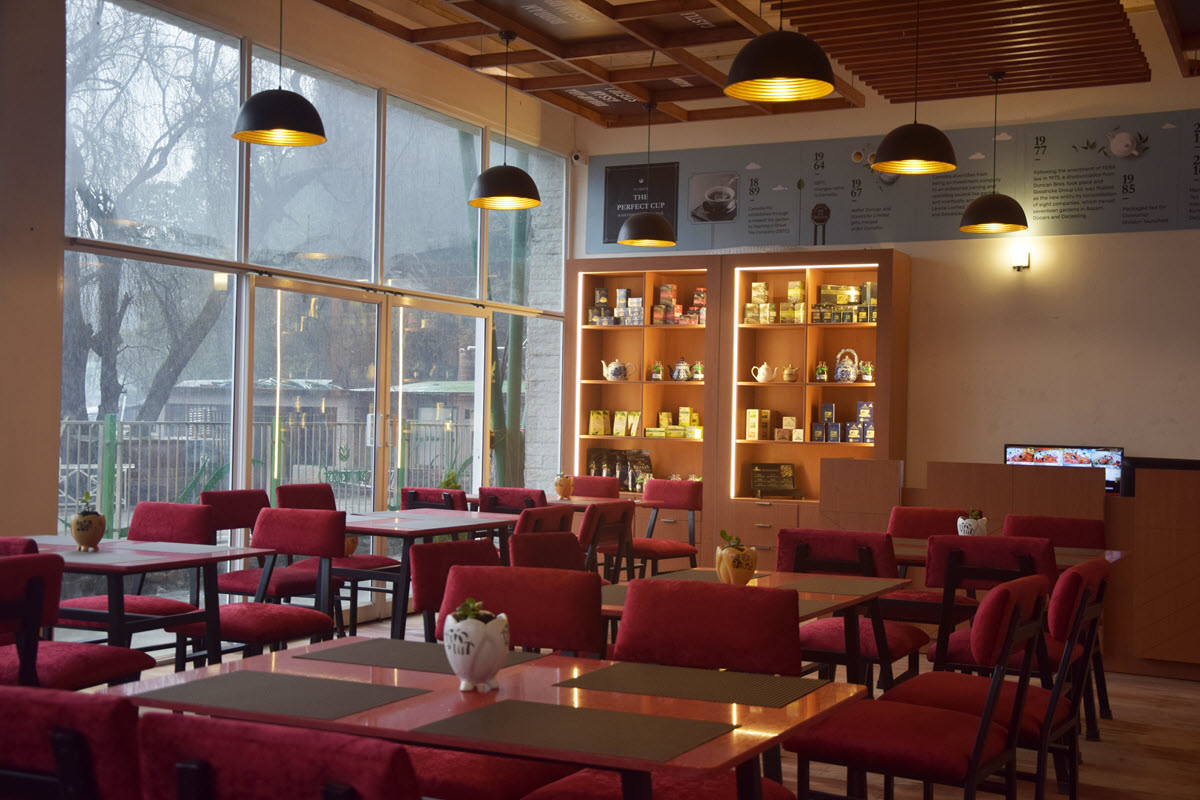
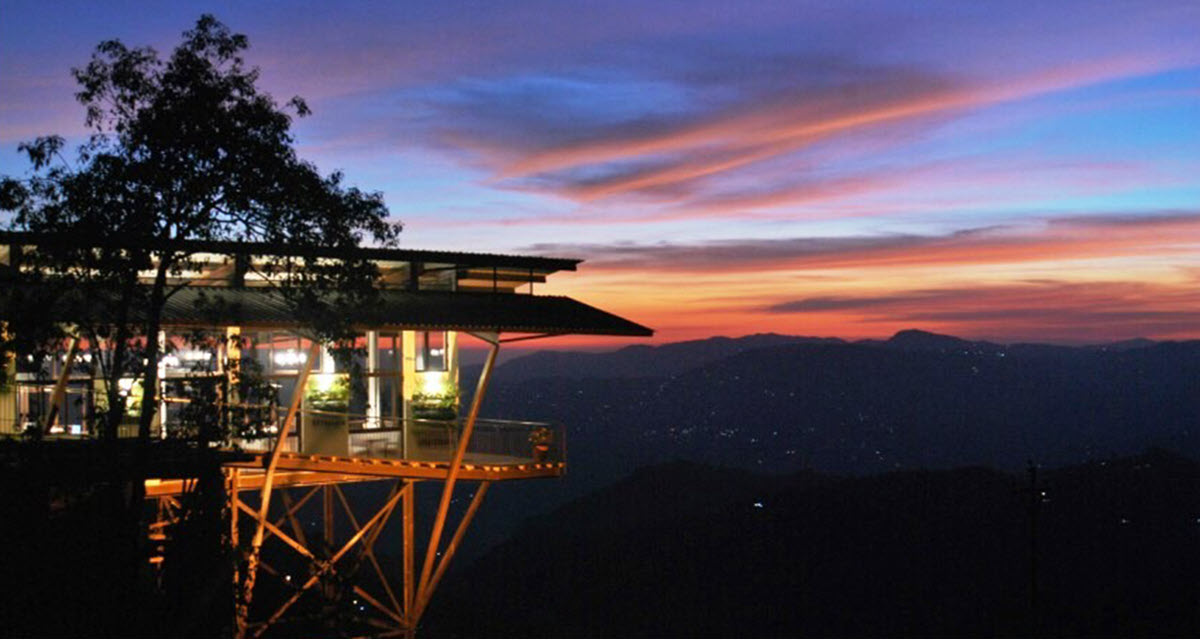
In 2016 Goodricke refurbished and rebuilt this stop to create Margaret’s Deck, a restaurant and tea lounge that overhangs the cliff and overlooks the valley. The tea lounge is now listed as the No. 1 restaurant in Kurseong on Trip Advisor. It is both a popular stop and a significant marketing asset that invites visitors to sample and savor the tea and purchase packets to take back with them.
Nothing sells tea better than sampling. The more people touch it and try – the more they buy. Goodricke opened more lounges, Queen’s Deck in Mumbai at the iconic Tea Board of India office, another one in Mirik, near their Thurbo Tea Estate, in Kolkata and Madhya Pradesh. The middle and north Indian belts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Punjab are important markets for the group. In Kolkata, they have found their most discerning audience. Goodricke’s roasted Darjeeling tea remains the highest-selling brand in Kolkata, a city of 15 million.
Long a hub for the British East India Company, the site of tea auctions, and a port city, Kolkata is the tea capital of India. It is the largest city in the state of North Bengal (the same state as Darjeeling) and is adjacent to Assam. Darjeeling tea is the tea of choice for the Bengalis but Kolkata is a massive and mature market for tea. It is also one of the few cities where the diversity of India’s taste for tea is on display. Notable among the more than 100 leaf shops include Lakshimi Narayan Tea House, Tearaja, Dhruba Tea Centre, Sharda & Sons, Subodh Brothers, Star Tea, and the Karma Kettle.
In Delhi, Mittal Teas opened in 1954 to sell a range of teas and continues to be the store of choice for connoisseurs in the capital. Nikita Mittal, who has joined the family business, speaks of how access to tea can influence customer preferences, “Every walk-in is treated like a VIP, try to give them the best experience. And once they have tasted a good quality tea, whichever they choose black, white, green, chai, they don’t like going back to the average teas. So, that’s how we try and do it – one cup at a time.”
“There is a restaurant in Gurgaon which is associated with us,” says Nikita, “The F&B Manager takes each and every thing about his beverages so seriously. How he presents the tea, the teapot, the timer… he educates the customer that you have to take it out in three or four minutes and that if you over brew it will ruin the tea if you under brew you don’t get the flavor. Those experiences matter and people always remember something better, that when they’re having a good time, a tea or coffee really added to the experience.”
In 2008-09, Dhiraj Arora and Priti Sen Arora started Karma Kettle in Singapore, as a restaurant serving Anglo-Indian food. The tea menu was a big part of the restaurant and its experience. They had a ringside view of the explosion of the beverage market, as brands began to offer custom blending, pairing tea and food. It was an eye-opening experience, they say. Five years later, in 2011-12, the couple decided to return to India. At that time, India was waking up to green tea. Dhiraj’s family owns and runs Cochrane Place in Kurseong, a boutique hotel with Makaibari, Ambootia, and Castleton tea gardens as neighbors. Buyers from Europe who stayed at Cochrane Place introduced Dhiraj to blending botanicals with tea. All of these experiences led them to embark on their tea journey.




In 2013, Karma Kettle launched as a tea brand, starting with ten teas that included four blends. As a brand, it reflects the couple’s aspirations — vibrant, youthful, with a love for travel. Their teas were marketed as “voyages in a teacup.” The teas were named for favorite destinations or a mood. “We wanted to give identity to a blend; we wanted our teas to ignite a sense of wonder,” says Priti.
Part of their success is attributed to the fact that India was not only a liberalized market, but the urban Indian was now well-traveled and keen to seek experiences, whether here or abroad. “Experience” is a word that comes up often in the conversation on marketing tea. In 2016, Priti and Dhiraj opened the Karma Kettle tearoom in Kolkata as a space for people to gather. “Tea is about community,” they say, and they hosted guests for talks, tea tasting sessions, food, and tea sessions pre-pandemic.
Proving that access to teas need not be upscale is the story of the tea Vandis. In the Nilgiris, tea vandis or trucks were launched last year by INDCOSERVE, the government-run cooperative of small farmers and bought leaf factories – the largest in India. In an earlier interview with Tea-Biz, Supriya Sahu (IAS), CEO of INDCOSERVE, had said, “Our factories were making losses. They did not explore other avenues, newer markets. They were quite content within the space that was made available to them… The tea market is volatile; we were vulnerable. Therefore there was a need for us to kind of explore other avenues. Why not explore selling packaged teas, that can be displayed on the shelf. If you want to sell, you have to create a brand.”
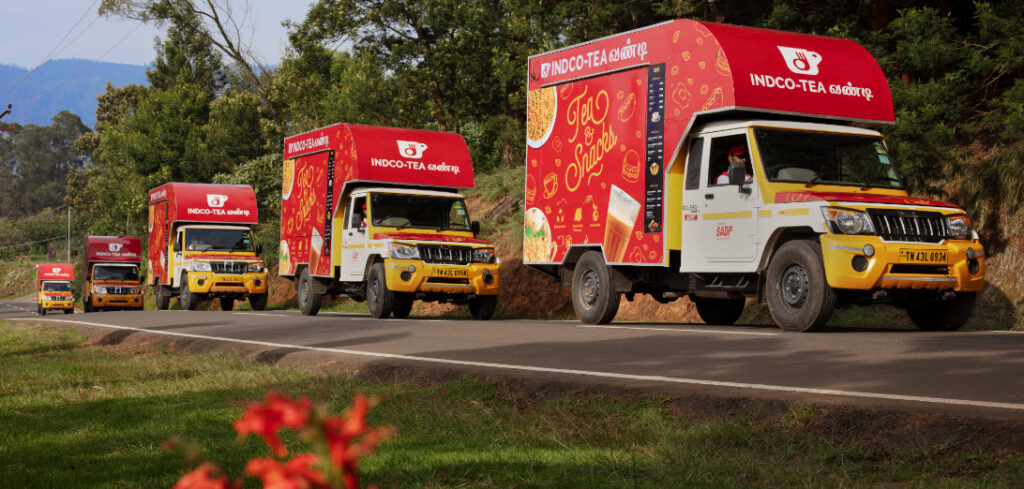

Sahu launched the Indco Tea House at Kattabettu and Bedford in the Nilgiris, but the striking red trucks parked at popular tourist stops in the hills are what have caught public attention. They serve tea – INDCO’s brand of tea – and snacks. “Our dream is that we should be like Café Coffee Day chain or Starbucks. Why can’t we, a home grown outlet, be like that?” Sahu had asked. INDCOSERVE’s branding and tea vandis show how even small farmers can retail and find an audience.
Online vs. offline
But no matter what scale or legacy, whether they have a store or long history, everyone’s now online. Despite a robust brick and mortar presence, Mittal too expanded to the online space, adopting e-commerce as an avenue for tea sales.
The extensive proliferation of mobile phones, access to the internet, and the burgeoning of smartphones have had a definite impact on the Indian consumer. It has also meant that it’s no longer the urban Indian who is the end consumer but significantly includes those who live in smaller towns, who aspire to a different way of life, and who can access products as quickly as an urbanite. The opening of markets has impacted consumption patterns, and it has led to several small brands coming up without the need to invest heavily in marketing.
However, e-commerce is not just a platform for brands. Producers now find that they too can retail. Luxmi Tea is one of such brands that branched into digital with the pandemic. In an earlier interview, Rudra Chatterjee, managing director of Luxmi Tea, had said, “This was the first time that we sold tea directly to consumers. And the reaction is amazing because, after all as growers of tea, it’s great to hear from someone who’s drinking that tea at home. Also, for us to get feedback one week or two weeks after we produce the tea… questions on how to brew the tea, pictures of how they are drinking their tea … It’s been energizing for me and my colleagues who are growing the tea in the estate.”
Jagjeet Kandal, industry veteran and currently Country Head, IDH, The Sustainable Trade Initiative, endorses it, “Producers are at the mercy of the market… If the market doesn’t pay them, what are you doing? You can’t keep blaming the market. As a businessman, you have to say, I will get out or change the business model. Every estate should put out 5-10% in packets.” It takes very little investment if one leverages online channels. If more producers did that, it could create the ripples of change because e-commerce and digital marketing have opened the tea market, as it did other FMCG products.
But there’s another side to this story. While starting digital, Karma Kettle soon opened a tearoom in Kolkata. Here lies another lesson: marketing tea is not exclusively choosing digital or offline but a blend of both.
Tea vs. blends
Karma Kettle does not own a tea garden. They see this as an advantage in the teas they bring their consumers. From tea farmers to suppliers of herbs and botanicals, they continue to service connoisseurs alongside those who seek flavored blends. Today, they have 100 tea blends.
The distinction in the market segment is essential. In Assam, Raj Barooah, after entering his family’s tea business, was attracted to the idea of retailing. He eventually started Rujani Tea, a specialty tea brand. In a blog post, he writes that 1999 and 2006 were the worst period for the tea industry in nearly a century. “Prices fell, productivity was low, and demand for CTC teas in the Indian market plunged. It was very, very difficult to keep going.”
From 2007 onwards, Barooah pursued the commodity trade, increasing his factory’s capacity. “But there was no joy in it for me. It brought back the old dream of doing something different, of creating a brand.” Traveling to China changed how he viewed the tea trade and his views on selling directly to consumers. Raj launched Rujani, named for his two daughters, as a brand that would represent the best whole leaf teas made at Aideobarie. Raj attempted to break the mold, assuming that Assam teas are CTC teas.
The pandemic certainly changed how producers and brands view the domestic market. In 2020, the lockdown was announced just as north India geared to harvest its first flush. Closing borders, stores, and hospitality meant that consumers turned online. And producers and brands took steps to meet them here.
Celestè was born during the pandemic, started by Anubha Jawar, who grew up amid tea in Siliguri. Celeste’s blends are their USP, with ingredients chosen to make them palatable to the Indian consumer. Here too, there is a focus on the experience. Celestè teas come in lovely packaging, but Anubha quickly points out that packaging is only part of the experience.
She would instead focus on conscious consumption, whether in the material used to package the teas, the tea bags, or the quality of ingredients used.
Celestè, like Karma Kettle, has succeeded in making tea appealing to a younger market by being a vibrant brand, more invested in flavors rather than tea’s snob value. Because that’s the other problem, Indian marketers will have to address — creating a new market for tea among India’s youth, something that coffee has succeeded in and will be hard to replace.
Coffee’s success in India is credited to Cafè Coffee Day (CCD), a brand started by Chikmagalur coffee planter Siddhartha VG. Back in the late 90s, he set up “cyber cafes,” which were spaces where one could buy coffee and surf the internet. The personal computer and the internet had not increased in homes yet, so this was a huge success. CCD became a chosen hangout spot for the young and continues to be a popular option 20 years later, despite the arrival of Starbucks. Jagjeet points out another learning from coffee. “See what coffee did,” he says. “They never boast of the amount of coffee they sold, they boast of tastes… this how they become icons. They are selling on experience.”
Chaayos and Chai Point are brands that constructed hundreds of outlets across the country, offering a range of teas and snacks. The audience for these are office goers who need a quick bite and want a reasonably good cup of chai. Both brands also offer chai in takeaway flasks that preserve the heat. A quick look at the menu points to what Indian consumers want — chai and green tea.
The newest brand to enter the fray is Teas from India, launched in December 2021 by Amalgamated Plantations Limited. “Our journey with tea is intertwined with the history of tea in India. With our 150 + years of experience and expertise, no one is better placed to unleash tea’s potential by bringing the best from bush to cup. Combining tradition and innovation to put quality first, our vision is to grow profitably and sustainably by serving as the industry pioneer of tea in India. In doing so, we wish to contribute and be present in the entire value chain of tea,” says Vikram Gulia, Managing Director at APPL.
APPL already had popular brands, some named for its estates, like Hattigor, which caters to the suburban and rural heartland and northern markets, and Majuli Mist; a roasted tea made for the West Bengal market. APPL launched Teas from India, targeting the millennial shopper looking for exclusivity and willing to pay the price for it.
Teas from India was chosen as the name to represent APPL’s legacy and the significant search engine advantages it offers, which is helpful as it is marketed more heavily on digital platforms rather than offline channels. The brand’s raison d’être is to showcase the diversity of India’s tea regions by acknowledging them, whether Darjeeling and Assam or the Nilgiris and Dooars and even Himachal and Sikkim. And taking cognizance of consumer preference, they offer a range of blends.
In the past regional preferences could be addressed by packaging various grades. Product diversification is more complex today, leading producers to keep up with trends — seen with the proliferation of butterfly pea flower tisane, turmeric blends, and, more recently, immunity teas.
The pandemic jumpstarted the category of immunity teas, and nearly every brand quickly added it to their portfolio, catering to a health-conscious Indian segment.
Green tea and chai
Green tea has risen in popularity in the last ten years; although it has been around for longer, it was made for an export base. Its marketing has been one of the recent successes tea has enjoyed, and the marketing narrative has hinged on its supposed properties to detox and help its drinkers enjoy wellness. Both Tata Consumer Products and Hindustan Unilever led the green tea marketing with TVCs, ads, and young Bollywood actors as ambassadors, emphasizing the influence mass media and big brands have in shaping consumer preferences.
But this has not been leveraged in creating a market for Assam orthodox tea. Ajay Jalan of Mokalbari Tea Estate and Chairman, Tea Association of India, says, “The cup that Assam produces — most of the consumers are not aware of it. We realize that more we give it to someone and get a repeat enquiry. The aroma and malty flavor that Assam teas have is not seen elsewhere. The market has blended teas of different origins and the true flavor of Assam tea is lost.” He adds that direct to consumer has started in a small way, but gardens don’t have the kind of resources it needs nor the marketing insight.
The market share lies with Tata Consumer Products, Hindustan Unilever, and Wagh Bakri. They continue to influence consumer preferences. Says Kandal, “The big packeteers are the ones who create the impression with the junta. Tea needs to be upscaled at even the lowest price point. Why are they not looking at explaining the value that even the cheapest tea brings to the consumer? If the poorest of the poor is buying it, he gets some value. Can they talk about the value?”
Jalan agrees, “The teas with major packeteers have been so commoditized that it does not encourage consumers to have more cups. Per capita consumption is still low.” He speaks of the need for a digital platform to promote Indian teas within the domestic and international markets. The Tea Association of India has proposed a Public-Private Partnership model, with producers and the tea board participating in creating the platform that will actively promote specialty tea.
Every tea producer recognizes the need to diversify and meet consumers halfway. Goodricke started making masala tea post-COVID. Their most recent release is a range of iced teas. Made from green tea sourced from their gardens, Badamtam and Barnesbeg, and bottled in glass, they see a successful pilot run in Delhi with Kolkata to follow. Dorje Teas in Darjeeling has launched a cold brew for the domestic market, Gopaldhara is making red oolongs, and Woolah in Assam is making bagless tea dips… there is diversification and innovation taking place, which may be the shift in India’s tea narrative.
But what of the consumer? Are they ready for a new way of drinking and enjoying tea? On the one hand, more than 50% of tea drinkers are from rural India, for whom price is a deciding factor. On the other hand, millennials with infamously short attention spans need to be hooked in the first 10 seconds of a post or a reel. The problem again returns to which India and which segment brands are pursuing. There is no one-size-fits-all formula. As many varieties of tea that the country produces, so too are the pockets that make up its markets.
What has changed is really access, anyone can order tea from anywhere in India, and more often than not, two-day delivery is possible.
“Tea needs to be upscaled at even the lowest price point. Why are brands not looking at explaining the value that even the cheapest tea brings to the consumer? If the poorest of the poor is buying it, he gets some value. Can they talk about the value?“
– Jagjeet Kandal, IDH The Sustainable Trade Initiative
Stories that sell
Rujani’s Raj Barooah chose to brand his leaves as whole leaf and not specialty tea. In his blog post, he writes, “I have come to realize that every specialty tea has to have a story behind it, sometimes true and sometimes, a better story than the tea. The success of this storytelling as a means to market the tea is evident, and has played an important role in birthing the category of specialty tea.”
For brands, “stories” are the marketing hook. And there are plenty of stories from the tea lands of India, whether history, conservation, culture, communities, or even ghost stories! But few have been able to exploit these stories memorably. The narrative continues to be half-hearted rather than sustained attempts to tell India’s story even though the customer seems eager to hear more.
Perhaps only Darjeeling has succeeded in offering customers a sufficiently intriguing story. There are many stories, from the story of young Margaret, who fell in love with the estate her father ran and promised to return but didn’t. Or, Jungpana and how it got its name from the dying and thirsty nobleman. One raconteur has used his skill to put his garden on the map: Rajah Banerjee, the former owner of the Makaibari tea estate.
When Rajah speaks of Darjeeling, it’s to describe it as a “magical, mystical land.” Rajah’s family-owned Makaibari for several generations, and in 1970, Rajah came home from England, where he was studying. In a tale he narrates expertly, he talks about how he felt the trees were calling to him to save them. One listens raptly as he speaks because he tells the story so well. Makaibari tea has reached the Queen of England in its time if one must measure its brand success. As a brand, it was ‘organic’ before that became a buzzword and ‘sustainable’ before we had even started talking about it.
“I was just having a love affair with this tract of land,” he says. “If you are passionate about whatever you do, whatever you’re committed to, you can market it. No tea is unsaleable. Every gram of tea can be sold. What you have to do is make that extra yardage to find a home for it.”
Makaibari has been a rare Darjeeling garden to market early to a domestic base. Rajah recounts being away in Berlin when he was at a store and saw a packet of tea that claimed to be Darjeeling but was “packed in Sri Lanka.” Before Darjeeling was granted protection of the European Union’s GI (Geographical Indication), it showed him how much had been given away in the opportunity.
In Darjeeling, Rajah opened up Makaibari to visitors. On weekends, he says, tourists arrived in large numbers, and every visitor got a tour of the factory and had a taste of tea. Everyone who walked out left buying a packet of tea. It was effortless marketing and helped build the brand. It was an experience people remembered.
For the mass market, tea has been sold on other narratives. One of the early TVCs for HUL’s Taj Mahal Tea featured tabla maestro, Zakir Hussain, endorsing the tea. Keeping the brand’s link to classical music intact, the most recent commercial for the Taj Mahal brand asks consumers to make time for tea even as classical music plays on, appealing to refined tastes.
Both TCPL and HUL have sought storylines that appeal to a higher ideal. For Tata, the Jaago re campaign was introduced in 2008 and is still in use. It started as a wake-up call to vote in the elections and expanded to various civic issues. HUL’s advertising covers many social issues, whether secularism, inclusion, or speaking up. Emotion and nostalgia continue to be compelling marketing narratives, especially for chai.
The challenge for new brands is in the lack of resources to match these expensive ad campaigns and find a narrative that is emotive and memorable and their own.
Because the best farm stories come from producers themselves, they are beginning to realize the interest consumers have in getting a peek into the world where their tea is grown and manufactured. And gardens are rich with these stories. Whether in how people live and work, flora and fauna, the plants, the factory… tea gardens are little worlds unto themselves; everything is potentially a story. An elephant herd passing through makes us stop and gasp with wonder; the paw print of a leopard on a muddy track is fascinating, as much as the journey of the leaf from the field, through the machines, and out.
The big question
Even as we speak of how digital is changing and transforming how consumers find, source, and access new teas, Raj Barooah voices caution. Sales are taking place on Amazon’s marketplaces, not the brand’s website. He points out. “Single digital websites like Rujani are not drawing traction. People prefer marketplaces. That’s where the whole thing is tilting. Even the bigger tea brands online are selling mostly on Amazon. “ He cites the story of Teavana in the US, the tea brand founded in 1997, bootstrapped but eventually reaching IPO and then bought by Starbucks for $620 million. “What became of Teavana? It peaked in success before a slump.” One reason cited is that its heavily retail presence could not keep up with online brands like DAVIDsTEA. “Are we still marketing tea?” asks Raj. “No one has found the growth curve. If Starbucks couldn’t, we are in serious trouble. There is a systemic problem in retailing tea. That’s the answer to the problem in marketing tea.”
“It is simple,” says Jagjeet Kandal. “Very, very simple. How do you move Indian consumption from the 780g? Get a hundred people in the room. Give them one question. Because there’s a role for the government to play in that, there’s a role for the marketeers to play there. And there’s a role for the producers. If we answer that question, we will have a solution.”
Maybe that’s the question, not whether people know about tea, or know how to source and brew it, and are willing to spend more on a better tea. Perhaps India’s tea marketing should begin with a single task of increasing consumption by one cup a day.
Realigning the Marketing of Indian Tea (Part 1)
Indian legislators are currently considering a draft Tea (Promotion and Development) Bill to remove colonial-era provisions regulating tea and re-direct the Tea Board of India’s resources to expand existing markets and promote tea domestically. Tea Biz explores the challenges and opportunities of marketing Indian tea by examining:
- A legacy of marketing tea as a blended, heavily spiced low-cost commodity beverage for the masses.
- The rise of hundreds of direct-to-consumer (DTC) tea brands that rely on e-commerce as a promising and accessible retail platform.
- Expanding choices available to tea lovers and how consumer preferences have moved beyond chai.

Nostalgia as a Trope in Marketing Tea
By Ramya Ramamurty | Branded in History
Nostalgia in marketing can be a double-edged sword – it may be twee to focus on quaint vintage designs or visual representation. It can also seem like a shamelessly exploitative marketing tool – to appeal to consumers in a way that borders on manipulative, like the low-hanging fruit of emotional recall. But when wielded correctly, it can be a lyrical exhortation to a more haloed historical era, to peddle something in the present by pointing out that the past is not all that different. It may inspire consumers to realize that in fact, in a lot of aspects, we are similar to our forefathers in what we want from life right down to how we eat and drink.
Taj Mahal tea has a rich storied advertising past that it frequently refers to in its current advertising. We don’t even have to go that far back. I doubt anyone can forget the visuals of the 1980s ad featuring Ustad Zakir Hussain’s head bobbing to the scintillating beat of his table and ending with the tagline “Wah, Taj!” It’s remarkable how the brand managed to forge a connection between a virtuoso performance by a percussionist maestro of classical Hindustani music, and the idea that the tea is restorative, as endorsed by an icon like him. But it clearly worked and one thing brand managers know is not to fix something that ain’t broke. In fact, things have come full circle with recent ads by Swiggy actually referencing this ad.
I think the use of nostalgia works if the brand is trying to spotlight a value that was successfully evoked in the past. It would almost be criminal not to leverage their own history. It is also a strategic way to ensure that consumers realize that their brand has a rich heritage in successfully creating and selling a great product. For instance, Wagh Bakri Chai was started 107 years back and may want its consumers to know that they have been around all this while, or that they started as a small tea brand inspired by Gandhian ideology way back when.
I think in the case of tea, nostalgia confers an immediate connection and grips the public imagination – reminding us of the tea we drank with our family, with friends, in decades past. It is still one of the first drinks we offer visitors and is a traditional beverage linked to Indianness despite its colonial origins, so it would make sense to leverage that in marketing it.
Link to share this post with your colleagues
Signup and receive Tea Biz weekly in your inbox.