Hear the Headlines
| Fairtrade International Predicts Climate-Related Disaster for Small Tea Farms
| Chemical Fertilizer Supplies Disrupted
| Holiday Helpers are in Short Supply
India Tea Price Watch
After a missed week of the auction, North India saw good demand in Kolkata, Guwahati, and Siliguri. Last week saw the highest weekly sale volume for 2021. In Kolkata, 83% of Orthodox tea on offer was sold, and the Middle East remained the top buyer. However, Darjeeling tea saw less uptake. In Guwahati, the market showed good demand for CTC and Orthodox teas, and major blenders were active. In Coonoor, buyers from North India were active, reportedly due to demand during Diwali, one of the biggest Indian festivals. Read more…
Features
This week Tea Biz travels to Lincoln, England for a visit with Will Battle, author of “The World Tea Encyclopaedia” and managing director of Fine Tea Merchants, Ltd., a wholesale tea import and export venture that supplies tea merchants with mainstream offerings as well as rare teas and herbals.

The Cost of Producing Specialty Tea
By Dan Bolton
Growers are taking initiatives on quality at all levels, blurring the lines between the everyday and specialty sectors, says tea wholesaler and author Will Battle. But is manufacturing specialty tea worth the effort?
“Frequently it probably isn’t considering the amount that growers need to invest from a financial and human resources perspective to make the very best teas,” he says.
The costs of producing the distinctive taste of the authentic, transparent, eco-friendly, clean-label formulations that are so popular with Millennial and Gen Z cohorts are significantly higher than what growers spend supplying conventional tea. A preference for chemical-free cultivation, third-party certifications, energy-efficient, carbon-neutral processing and transport, and recyclable and biodegradable packaging further erode margins along the length of the supply chain. Consumers who pay a premium at retail for specialty tea often leave growers to foot the bill. This raises a fundamental question: Is anyone making money making specialty tea? Read more…
Listen to the review
News

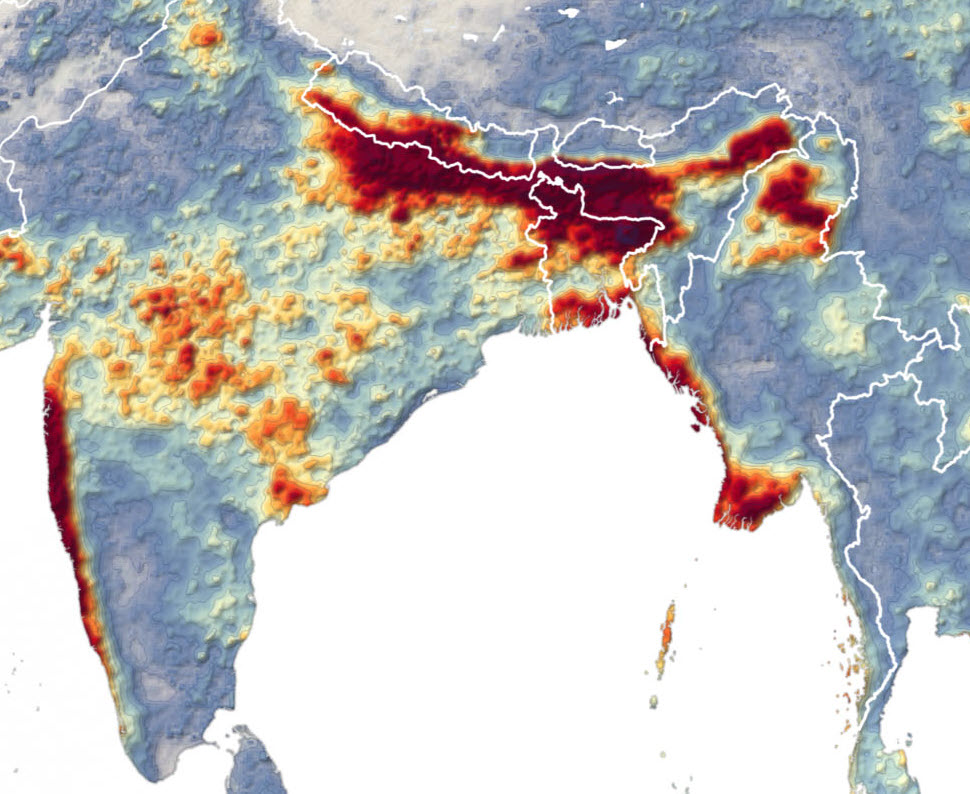
Fairtrade International: Small Tea Growers Face Climate-Related Financial Disaster
Limited access to capital will make it difficult for farmers to finance adaptations to changing climate that will generally lower yield, reduce tea quality, and lead to more instances of catastrophic failure in tea “hotspots” globally.
By Dan Bolton
According to Fairtrade International, a hotter and drier climate poses a severe financial threat to millions of farmers in major tea-growing regions.
The third-party certification organization released a 148-page report ahead of the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland (COP26). Fairtrade CEO Nyagoy Nyong’o called the study’s results “extremely alarming and a clarion call for immediate and comprehensive climate action.”
The study assessed climate impacts on bananas, cocoa, coffee, cotton, sugarcane, and tea producers. Juan Pablo Solis, Fairtrade’s senior advisor for climate and environment, said, “the way climate change affects the planet is extraordinarily complex.” He cited “mounting challenges that they [Fairtrade International certified farmers] face if the international community continues to fail them.”
In summarizing the impact on tea, the authors state that tea-producing locations will be subject to considerable increases in the number of days of extreme temperatures, especially under the high emissions scenario.


Chemical Fertilizer Supplies Disrupted
By Dan Bolton
Closure of fertilizer manufacturing plants in the UK and record-high prices approaching $1,000 per short ton in North America foretell cutbacks as global food prices reach a 10-year high. There are ample stocks and capacity, but timely arrival is a concern due to the shipping crisis and fertilizer prices are prohibitively high for some applications due to rising energy costs.
China, the world’s largest agrochemical manufacturer by tonnage, cut output due to rising energy prices but has since allowed manufacturers to maintain high operating rates to meet domestic food security requirements. Fertilizer exports surged in 2021 with a total of 10.8 million metric tons during the first eight months of the year, an increase of 46% compared to the same period in 2020. In July China suspended phosphate exports and in August exports declined by 26% to 2.78 million metric tons.
As prices spike across a broad range of plant nutrients European growers say they may be forced to idle croplands or plant less fertilizer-dependent crops than corn, for example.
In the US the price of urea increased 26% in the past month reaching $0.80/lb.N [per pound of Nitrogen] with anhydrous at $0.57/lb.N., an average $940 per ton. Potash is up 15% compared to September.
Biz Insight – The disruption is troubling because tea is a very demanding plant requiring 300-450 kilos of Nitrogen per hectare for high-quality shoots plus three secondary nutrients and 10 trace elements. No soil in any part of the world can continuously provide full nourishment for plants producing economically significant yields without fertilizer.

Holiday Retail and Delivery Workers in Short Supply
Workers in US retail and warehouse fulfillment are in high demand and short supply as major employers’ staff up for the holidays.
Seasonal culinary workers, delivery drivers, and retail clerks are among the 4.3 million “missing workers” unable or unwilling to return to work, according to the Wall Street Journal. Money Magazine notes that 10% of seasonal job postings on Indeed.com include the description “urgent.”
Amazon expects to hire 150,000 seasonal workers (up 50% from 2020) and is paying an average of $18 per hour. Supervisors can qualify for $3,000 signing bonuses in key slots. UPS is advertising warehouse and package-handler jobs at $22 per hour. Walmart, Target, and FedEx round out the top five seasonal employers with a combined 600,000 slots to fill.
In response, smaller retailers and cafés are offering additional hours and more stable work hours to existing employees, investing in staff training, and promising to transition the most promising new hires to full-time work in 2022. New hires are requesting more flexibility and benefits. The shortage means seasonal and full-time job seekers have greater leverage this year to negotiate bonuses and benefits and wages greater than $15 per hour.
Biz Insight – There are 10 million US job openings as workers quit at the highest rates on record. Nearly 50% of US adults in a recent LinkedIn survey said the pandemic has changed how they feel about their careers. Of those who view their careers differently, 73% said they felt less fulfilled in their current jobs. The greatest decline in the eligible worker participation rate is among women, workers without a college degree, and those in low-paying service industries such as hotels, restaurants, and childcare, according to the Wall Street Journal. Pandemic accelerated early retirements among those 55 and older is a trend that economists say is unlikely to reverse.
— Dan Bolton
- Read more… links indicate the article continues. Learn more… links to additional information from reliable outside sources.
Upcoming Events
November 2021
Coffee Fest | Nov. 5-6 | Portland, Ore.
Oregon Convention Center | Education Program | Registration
HX: The Hotel Experience | Nov. 14-15 | New York City
Jacob Javits Convention Center | Agenda | Register
Click to view more upcoming events.
Share this episode with your friends in tea.
Listen to Tea Biz on Apple Podcasts
https://teabiz.sounder.fm/episode/news-01212021Subscribe and receive Tea Biz weekly in your inbox.