New study recommends motivational campaigns, demonstrations, training, and extension work to encourage growers large and small to adapt to climate change.

Tea Garden Managers in Assam Confront Climate Change
The threat of climate change looms large in tea. “There is increasing evidence that climate change will strongly affect tea cultivation,” concludes a study of growers in Assam, the world’s top tea producing region.
Garden managers in Assam are responding to the threat with adaptive measures that growers will find useful in many tea lands. These include rainwater harvesting to enable irrigation during dry spells, reforestation, conservation of biodiversity, soil mulching, and the creation of wind barriers that combine to mitigate the threat.
To better understand the seriousness of the situation and to discover local adaptations, two scientists at the Tocklai TRA (Tea Research Association) in Jorhat sent questionnaires to growers in four regions of Assam – Upper Assam, South Bank [of the Brahmaputra River], North Bank and Cachar. Combined, these regions produce about 12% the world’s tea, supporting the livelihood of 1.2 million workers.
The study Perception of Climate Change and Adaptation Strategies in Tea Plantations of Assam India analyzed tea growers’ awareness of climate change, its impact on tea, adaptive approaches undertaken and future strategies. The study was recently published in Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, a peer reviewed, scientific journal published by Springer. The work was authored by Dr. Pradip Baruah and Dr. Gautam Handique at Tocklai.
The scientists note that climate change is a global concern with impacts that vary at the farm level. The majority of respondents were aware of changing climate conditions and the effect on tea production. How farmers respond to climate change needs to be precisely understood if the government, policymakers and researchers are to effectively support adaptive and mitigative approaches for the tea crop. Data was received from 83 tea estates.
The impact of higher temperatures, erratic and often torrential rains are evident, according to Dr. Baruah, monitors weather and growing conditions and regularly shares his findings and advice online like in this March 15 tweet: “Rainfall has been quite scanty so far this year in Assam tea areas. Irrigation is still on in a Golaghat area tea estate today, which is mid of March.”
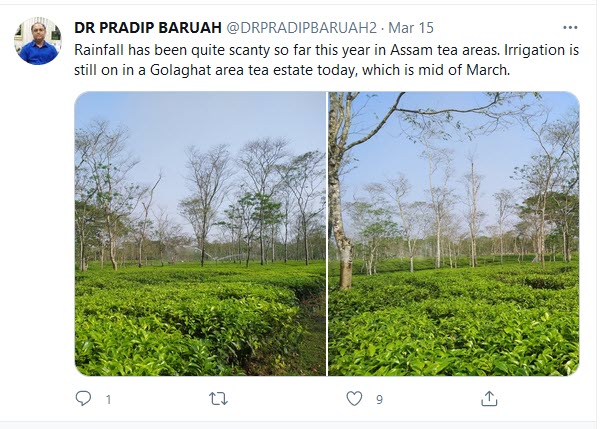
Rainfall has been quite scanty so far this year in Assam tea areas. Irrigation is still on at a Golaghat area tea estate today, which is the mid of March. – Dr. Pradip Baruah
The study revealed that most respondents (85.5%) were ‘deeply concerned’ about climate change, 9.6% were ‘somewhat concerned’ and only 4.8% were ‘unconcerned’ regarding climate change.
Three quarters of respondents (78.3%) reported a decline in productivity while 12% were uncertain. Only 9.6% of the respondents suggested that tea production was not vulnerable to climate change. Respondents from gardens along the South Bank of the Brahmaputra River report the greatest impact, followed by North Bank growers and those in the Cachar region. A majority in every region confirmed that climate change, visible as spikes in temperature, drought, and variations in rainfall, was significantly affecting their crop production.
Tea depends greatly on rainfall for optimal growth. Leaf productivity and the bushes are harmed by either an excess or shortage of water. Respondents said adverse conditions such as prolonged drought during winter and/or periodic heavy rainfall in recent years pose a threat to the sustainability of the crop.
The study pointed out that rains have become unpredictable with some regions suffering from prolonged dry spells, while other experience incessant rain particularly during the monsoon months. Respondents said climate change has also led to an increase in insect and disease infestation.
In July 2020 the Brahmaputra River inundated around 26 districts, driving 2.8 million from their homes and killing 123.
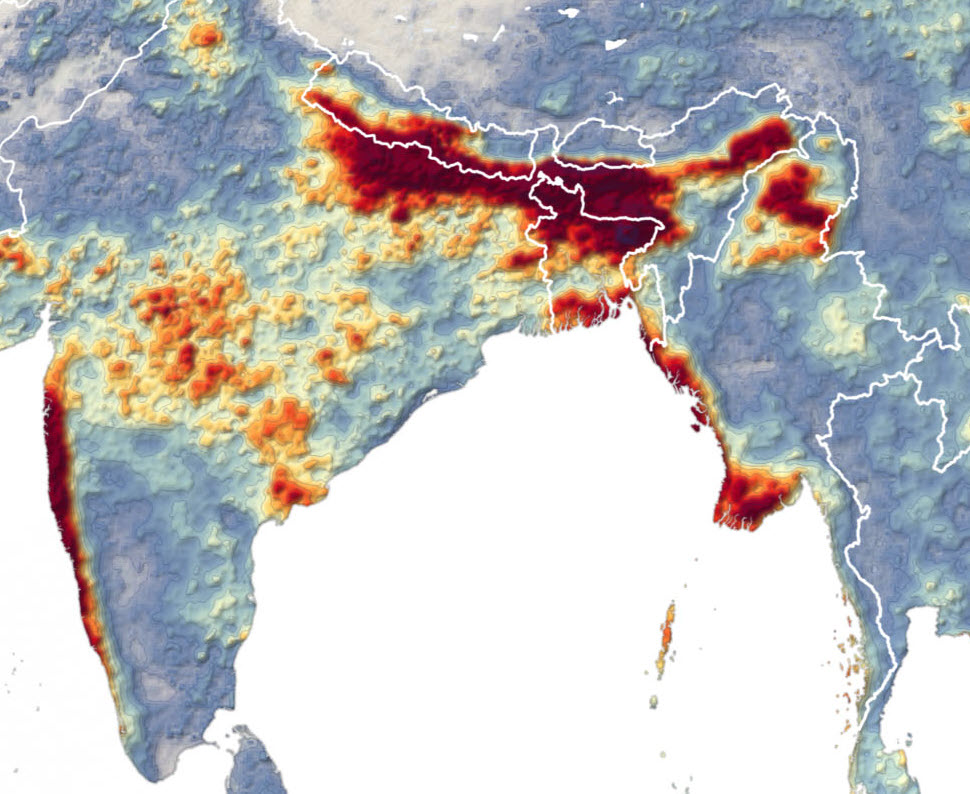
Assam recorded 1,164mm of rainfall compared to a normal monthly average of 894mm during July 2020, an excess of nearly 30% (see map). The catchment areas of nearby states, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim also received excess rainfall 16% and 45%. – NASA Earth Observatory
“As future management strategies, tea growers have opted to gradually replace synthetic fertilizers with organic manures and pesticides, construct anti-erosion measures along river sides and embankments, and generate awareness programs” according to to the study.
Adaptive Measures
The Rosekandy Tea Estate in Cachar in South Assam anticipated the local impacts of a changing climate as early as 1982.
Ishwarbhai Ubhadia, general manager at Rosekandy TE, told Tea Biz, “We have created rainwater harvesting ponds all over the estate. We now have a 100 hectare area under water,” he said. “Wind belts have been created and we have maintained 500 hectares of reserve forest to maintain micro-climate and ecological balance,” he said. Installation of 70- kilowatt powered solar plant is underway. The generator will be commissioned by April, he said, adding that hunting of birds and animals on the land is now prohibited.
Garden managers expressed optimism in applying strategies to mitigate climate change. Rainwater harvesting and irrigation are now common in Upper Assam and along the South Bank, North Bank and Cachar. Adaptive measures like reforestation programs and the creation of wind barriers were mostly implemented in Cachar as compared with Upper Assam. Cachar and South Bank gardens are more likely to practice of soil mulching compared with the North Bank.
In-situ water conservation largely consists of constructing artificial ponds and lakes and developing existing natural water bodies such as streams, rivulets, swamps, and low-lying areas. “Rainwater harvesting increases the amount of water per unit in cropping areas, reduces drought impact and enables the use of run-of beneficially,” according to the study.
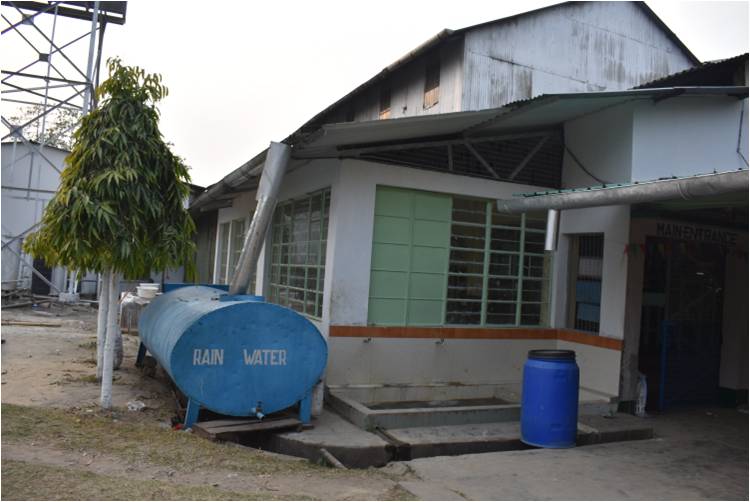

Rooftop harvesting at Heeleakah Tea Estate is low cost and effective. Water is stored and used for consumption, tea tasting, dehumidification, etc. In the garden, rainwater ponds and reforestation programs establish a microclimate ideally suited to growing tea. Photo by Dr. Pradip Baruah.
Photo by Dr. Pradip Baruah.
Mulching conserves soil moisture, reduces surface runoff and soil erosion and lower soil temperature. To minimize the impact of wind speed, respondents are constructing wind barriers to deflect high velocity of winds that increase evapotranspiration and desiccation, lodging in young tea plants, uprooting of shade trees, etc.
Dr. Baruah says the impact of climate change is readily evident. “The first and second flush tea is getting affected. More needs to be done with regard to ecological micro-management by planting various types of trees,” he said.
“Climate change is dynamic, impacting all but it needs a total approach at global and local level,” writes Dr. Baruah. “The good thing is that the tea estates have the capability of doing it to a great extent in different topographical and agro-climate conditions. Results are absolutely visible in Cachar area tea estates and in other areas of the state,” he says. “It is never too late but trying to adapt and mitigate the effects of climate change is the only way ahead,” he said.
The study says coal and natural gas are extensively used in tea production and can be gradually replaced with new, cleaner technologies. “However, the cost economics, availability and energy efficiency standards of such ‘green energy’ will have to be properly worked out before essentially implementing in tea plantations. Similarly, the gradual replacement of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides with organic ones will be a welcoming step, but at the same time, one has to look at the practical feasibility and cost economics of such implementation” the scientists involved in the study say.
Plan of Action
The proportion of tea plantations proposing future strategies like planting of tolerant/resistant tea cultivars and awareness and training programs among workers and associated people is higher for South Bank and North Bank as compared with that of Upper Assam. The proportion of tea plantations proposing future strategy of awareness and training programs among workers and associated people were in favor of South Bank and North Bank, respectively.
Scientists say the present study will be helpful to make more informed future strategies regarding best practices for tea cultivation under a changing climate for tea-growing regions all over the world.
The Way Forward
During a virtual International Tea Day panel discussion last year, FAO Director-General, Qu Dongyu, cited the importance of achieving greater sustainability in the tea sector. Panelists agreed on the need to develop strategies for climate change adaptation and mitigation, promote market transparency and sustainability of the tea value chain and develop policies for sustainable tea production benefiting, first and foremost, smallholder farmers. FAO has since launched projects to develop carbon-neutral tea cultivation (see below).
FAO’s Intergovernmental Group on Tea when it last met formally in 2018, warned that tea cultivation and production globally is facing climate-related challenges which need to be addressed. Delegates concluded that “Climate variability, incidents of frost and prevalence of pests, also have an influence on tea production, and are beginning to affect productivity.”
The Assam study calls for motivational campaigns, demonstrations, training and extension work to encourage adoption of climate change. “The implementation of long-term policies for climate change by the government needs to be strengthened so that the benefits reach every tea plantation and if necessary, subsidiary schemes can be developed by the government to encourage more adoption of such techniques” the study says.

FAO Launches Carbon-Neutral Tea Project in Kenya
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is working with tea growers in Kenya to pioneer carbon-neutral tea.
The program attempts to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions at each stage in the tea value chain.
The project will use carbon-neutral tea production methodologies developed in China by the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) as well as new technologies to tackle climate change through energy efficiency, tried and tested in the Kenyan tea sector by the German Development Agency (GIZ).
Scientists will prioritise energy and resource efficiency in tea factories through technology transfers, implementation of effective monitoring management, green procurement guidelines and factory automation.
The project will also address the first stages of the tea value chain and the cultivation of tea bushes using low carbon practices including the reduction of fertilizers and pesticides, the support of carbon sequestration and soil conservation.
Resource Links
International Trade Center
Mitigating Climate Change in Tea Sector (2014)
Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Carbon-Neutral Tea Production in China (2019)
FAO Intergovernmental Group on Tea (23rd Session)
Fostering Sustainability in Tea Production (2018)
A link to share this post with tea friends and colleagues.
Subscribe to the Tea Biz newsletter and view archive
Subscribe and receive Tea Biz weekly in your inbox.

