In October, Transworld, China’s first USDA-certified organic tea producer, and Firsd Tea, the US subsidiary of Zhejiang Tea Group, released the Chinese Tea Sustainability Report, a 12-page survey of perspectives and practices at Chinese tea farms and processing facilities. The report tracks closely with Firsd Tea’s annual Sustainability Perspectives survey. Operators who responded generally comply with emerging traceability standards and guidelines by third-party certifiers, including the Rainforest Alliance, FLOCERT (Fairtrade International), and Fair Trade USA. Respondents from the nine provinces surveyed collectively produce 15 million kilos of mainly green tea on 12,000 hectares of land.
Listen to the interview.
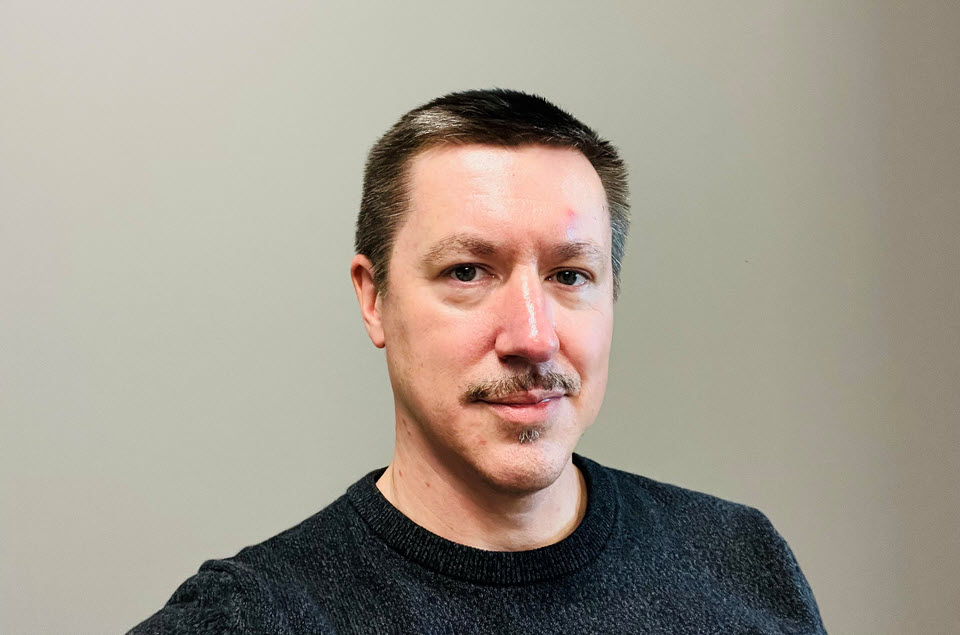

Sustainable Tea Plays a Critical Role in Alleviating Poverty
By Dan Bolton
Jason Walker, 46, one of the architects of the sustainability report*, is the marketing director at Firsd Tea in New Jersey. His expertise includes business development, market research, and tasting. In June 2019, He testified at the US Trade Representative Hearings on behalf of the US tea industry in opposition to increasing tariffs on Chinese tea. “I really enjoy marketing as a bridge for sharing what’s new and relevant,” he says. “My connections to China and my work with Firsd Tea provide a great opportunity for thought leadership to and from the Chinese tea industry.”
Dan: Jason, let’s begin with some background on China as a responsible agricultural producer.
Jason Walker: In the past few years, China’s strategic plans have emphasized reducing pollution. More recently, they shifted towards food security. And they’ve said, ‘Let’s keep that green. Let’s keep that clean. But let’s alleviate rural poverty and bring in more food security as well.
Dan: China has demonstrated a long-term commitment to alleviating rural poverty. Describe the role tea plays.
Jason: When you take a more extensive view and look at what the UN says regarding global economic development and people emerging from poverty, much of that success can be attributed to what China has done within China. You’re talking about a lot of people that China by themselves; World Bank estimates range as high as 800 million — that China has helped get out of poverty.
Tea has been a useful way to do that because the tea product is a leaf, it is a stable, sturdy plant, you’re not tilling it up and planting something new, you’ve got a good product, you can learn you can train people on how to grow it well. And they have a regular crop every year to give a steady income.
It was a reason to develop a lot of rural areas. Because now you’ve invested in that leaf and the infrastructure, they need to be able to sell and produce that leaf.
China set [sustainability] standards, especially domestically, for tea. About 85% of China’s tea stays in China. They said, ‘We have to protect our people and raise our standards internally as well.’
Most respondents now have an improved outlook on progress made in sustainability in the last ten years. They also view present-day efforts more favorably and predict an increased improvement trajectory in the next ten years.
Firsd Tea Sustainability Perspectives 2023
Dan: Will you dig a little deeper into the specifics of the Chinese Sustainability report?
Jason: Our Sustainability Perspectives is a global report that looks at professionals from tea, coffee, and cocoa and compares their different perspectives.
What we saw was that a lot of people are still concerned about the environmental aspect of sustainability. They are worried that tea is more susceptible to climate change than other crops like coffee and cocoa. So that was a bigger concern.
But when we asked: What are you prioritizing in terms of sourcing products to sell? They’re still prioritizing taste, price, and leaf characteristics. In some cases, organic comes to the top above things like sustainability. So there seems to be a mismatch in priority, and maybe the talking points behind it.
In 2023, respondents still listed flavor (96%), leaf grade (91%), and origin/terroir (90%) as the top three characteristics that contributed to their decisions to stock particular tea types. Respondents in tea and related industries ranked “Sustainability” in the bottom three purchasing drivers, edged out by demand, consistency of supply, and price.
Firsd Tea Sustainability Perspectives 2023
Dan: How influential are the third-party certification partnerships that have been established? Transworld, for example, was China’s first USDA-certified organic tea producer.
So you’ve got Rainforest Alliance, you’ve got Fairtrade. They are active in China, although China isn’t their most well-known market or area of influence because China already has fairly high standards set by the government. Many Chinese producers already comply with pretty high standards to operate within their country, which makes it a little bit easier for fair trade certification to some extent rainforest as well to say that they’re already in compliance.
The end you must meet are EU standards for imports and US standards in terms of pesticide residue levels and, increasingly, overall traceability and more government requirements in places like the EU and the US in terms of protection of workers. Deforestation and other areas are becoming new laws in the pipeline.
“Respondents in tea and related industries still believe Organic Certification is the most important standard to consumers (95% of respondents). Non-GMO has surpassed Fair Trade as the second-most important standard.”
Firsd Tea Sustainability Perspectives 2023

Dan: In April 2018, Transworld and Zhejiang Tea Group donated 15 million green tea seedlings to villagers in 34 poverty-stricken areas across three provinces. Five years later, 1,800 households and more than 6,600 family members are thriving thanks to increased income from tea. Will you discuss the impact of the White Leaf Sustainability project?
Jason: Some research institutes in China and local and regional government organizations said, ‘We have healthy farms in Zhejiang province that are prepared to donate millions of tea seedlings or cuttings and distribute those within rural, underdeveloped areas in Western and Central China. And they brought those into those villages, and they not only showed villagers how to cultivate those plants, but they also invested in the local processing facilities.
They contracted in terms of committing to buy X number of kilos from those facilities. And marketed those teas as unique, valuable products that benefit these communities and build them up to be sustainable. As you said, it’s not just about the planet but also about the people.
Dan: What motivates the Chinese ag industry to strive for sustainable production?
Jason: They want their citizens to have a clean and healthy environment. They are looking for how they can ensure that our people are healthy, have good job opportunities, have growth, and feel that their products are safe. So that’s why they’re aiming even for zero growth in some pesticide applications. They have put more research into converting from the more conventional pesticides to biopesticides and non-traditional pest solutions, like light traps.
They’re doing the research and development stage where light traps had different wavelengths. Some attract the male insect, and some attract the female insect to keep them from mating. So they’re looking to cut back on the conventional to bring in more novel solutions to be sustainable, clean, profitable, and growing.
Dan: The report is an admirable effort to monitor tea sustainability globally, Jason. Let’s close the discussion with this open-ended question. What are pressing challenges, and what does the future hold?
Jason: First off, what I see for the future is that I think we can reduce the traditional conventional pesticides, especially where those are heavily monitored. We are exploring how to move towards bio-pesticides that are plant-derived or more naturally derived solutions.
How do we ensure the rest of the world is on board to recognize them as acceptable solutions and optimized practices worldwide? With that in mind, how do we protect people as their concerns about migration of people moving, how does that affect tea harvesters who are moving around to different harvest locations, and how will they be looking at the timing that affects the seasons and harvest times?
So, this year, 2023, has been better so far than 2022.
The Meteorological Society, from what I’ve heard, is discussing how to provide better projections and practical advice to the farmers — what to prepare for, how to adjust your pruning, how irrigation may be maybe improved in terms of rain retention ponds, drainage channels, or ditches that capture more moisture, those types of things.
Generally, everybody in tea doesn’t want to rock the boat by saying changes in climate are affecting quality — yet. They feel we can still make the most out of what we’re doing.
There are lots of issues to work on. There’s a great opportunity to touch on all those things if we, as we talked about in the studies, can all get on the same page in terms of communicating about these things, sharing our concerns, and working on shared solutions.
“When it comes to specific climate change threats on tea production, most respondents said changing rain patterns (95% in 2022 vs. 100% in 2023), and extreme heat (91% in 2022 vs. 97% in 2023) are the biggest climate change risk factors with pest problems close in third (89% in 2022 vs. 96% in 2023). Paralleling worries about the effects of climate change on business operations, 95% (vs. 93 in 2022) of respondents said that tea is a very or somewhat sensitive industry to the effects of climate change, followed by coffee at 86% (vs. 82% in 2022).”
Firsd Tea Sustainability Perspectives 2023
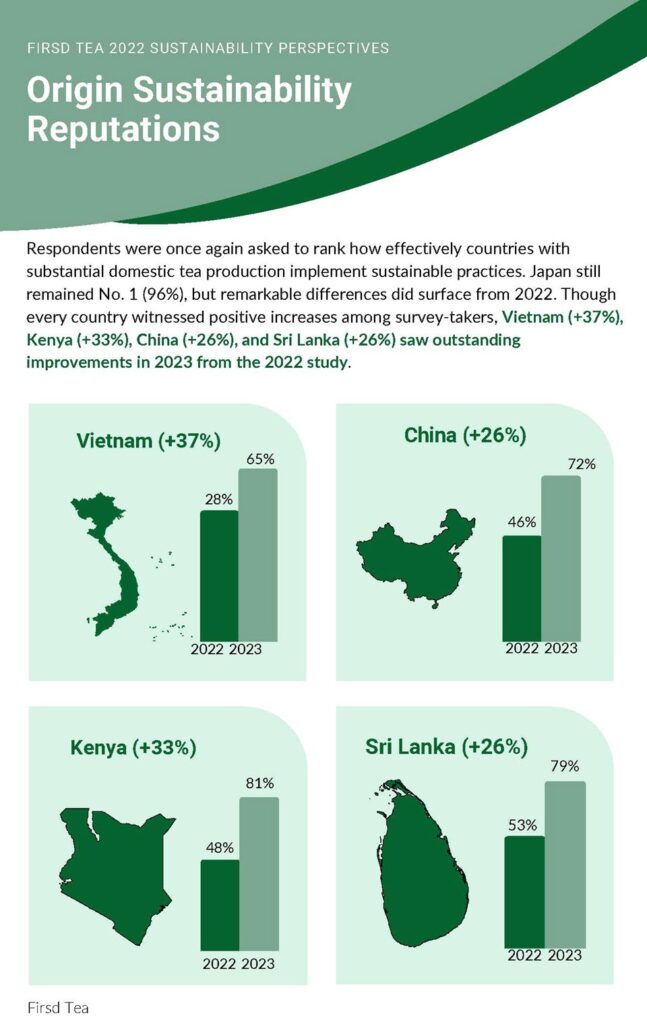
Respondents were once again asked to rank how effectively countries with substantial domestic tea production implement sustainable practices. Japan remained No. 1 (96%), but remarkable differences surfaced in 2022. Though every country witnessed positive increases among survey-takers, Vietnam (+37%), Kenya (+33%), China (+26%), and Sri Lanka (+26%) saw outstanding improvements in 2023 from the 2022 study.
Firsd Tea Sustainability Perspectives 2023
Respondents Most Commonly Mentioned These 5 Themes
- Consumer Demand – “All actors in the supply chain need buy-in. Consumers want [sustainability] but don’t want to pay for it. This forces producers to comply with standards without getting increased pricing.”
- Quality of Life for Workers at Origin – “Paying a living income to the industry, especially smallholders, will help promote sustainability practices.”
- Better Farming Education – “More education and training to farmers.”
- Environmentally Responsible Practices – “Using more eco-friendly methods of farming and processing.”
- Improve Regulatory Programs – “… sustainability certification programs must engage with the local laws, tea research bodies, and technological experts. By doing so, they can provide meaningful benefits to tea farmers and ensure their economic sustainability.
Consider…
Research done by Stanford University suggests that helping smallholders optimize their use of pesticides could be a big win in terms of reduced environmental impact. Globally and in China, the majority of tea is farmed by smallholders.
*The Sustainability Perspectives report derives its findings from a three-month-long survey administered by Crothers Consulting to 100 voluntary respondents conducting business in tea and related industries(e.g., coffee, sugar cane, wine, and cocoa) on behalf of Firsd Tea. Survey responses were primarily generated by website posting and subscriber outreach by Firsd Tea and The Tea& Coffee Trade Journal, direct messaging on platforms like LinkedIn, and word-of-mouth networking. Industry-specific organizations, including the Tea and Herbal Association of Canada, promoted the survey by sharing it with virtual conference-goers.
Powered by RedCircle
Share this post
Jason Walker, Marketing Director at Firsd Tea in New Jersey and one of the architects of the newly released Chinese Sustainability Perspectives report joins Tea Biz for an in-depth discussion of the results of this ongoing survey.













