
Tea tasting webinars
Marketing is one of the most costly and daunting challenges for rural tea entrepreneurs in emerging markets. Digital marketing necessitated by the coronavirus pandemic adds another layer of complexity.
Since December seven artisan garden owners have combined their resources to present inexpensive virtual garden tours with live cupping attended by as many as 50 qualified buyers from around the world and a least one curious journalist.
The hour-long webinar on Feb. 18, hosted by the Ceylon Artisan Tea Association (CATA) and Kaley Tea Estate, is the third in the series. Buyers from major retail ventures in France, Japan, the U.S., and across Europe saw a brief PowerPoint explaining the association’s history and objectives, then set off on a trek into the tea forest where 150-year-old trees rise 30 to 50 feet toward the sky. The plot, formerly a pruned commercial garden, was abandoned and has since returned to its biodiverse tropical ancestry but this forest canopy is uniquely dominated by tea.
CATA began in 2019 as a collective based on a shared vision that focused on efficient micro-production that, in aggregate, could scale. It is a community-centric model that can be adapted by rural entrepreneurs in many tea lands.
The seven small enterprises have limited resources individually but collectively provide buyers diverse offerings in style and the distinct terroir of Sri Lanka’s growing regions. CATA expects to recruit additional gardens representing Nuwara Eliya, Dimbula, Uva, and Uda Pussallawa in the high mountains, Kandy mid-country, and Ruhuna and Sambaragamuwa in the low altitude coastal zone.
Estates are small. Amba grows its tea on only 30 acres. Neighboring farmers grow the remainder. But the price that Amba pays per kilo for fresh leaves is more than double the average in Sri Lanka. High rates encourage locals to grow tea naturally, adhering as close to organic cultivation as possible.
Last year the pandemic quickly decimated the island nation’s tourism sector. Tea sales to foodservice establishments declined at every level. Growers began the webinar series to maintain existing business relationships and later found ways to attract new buyers globally. Each garden sells most of its tea locally, but for overseas buyers, watching these videos offers tea retailers and wholesalers an alternative to sourcing in person during travel restrictions and mandatory quarantines.
The Zoom webinars are recorded, see for yourself.
- Kaley Garden Tour and Webinar, Feb. 18, 2021. Cupping: White Teas
- Forest Hill Tour and Webinar, Jan. 14, 2021. Cupping: Green Teas
- Amba Tea Estate Tour and Webinar, Dec. 10, 2020. Cupping: Black Teas

A student intern with promising skills as a videographer followed Kaley Tea director Udena Wickremesooriya through the plucking, rolling, and processing steps, capturing Udena chatting with workers and pointing to innovations such as locally built drying racks and equipment customized to make the creative shapes.
Cupping table
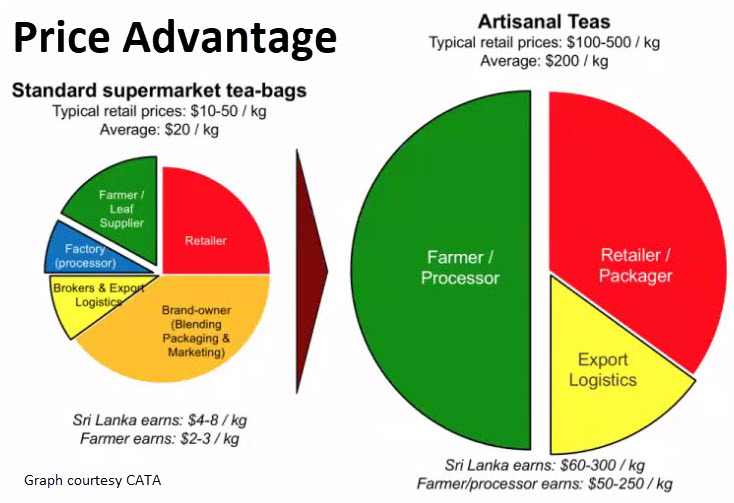
Cuppings and the accompanying tasting notes are critical to effectively market artisanal tea. Seventy-five percent of consumers consider taste the most important consideration in choosing tea. No matter how compelling their brand story, growers rely on sampling to seal the deal, but no one has the time to sample all the tea in the world. Webinars that enable face-to-digital-face interaction and user engagement will likely continue long after the pandemic resides.





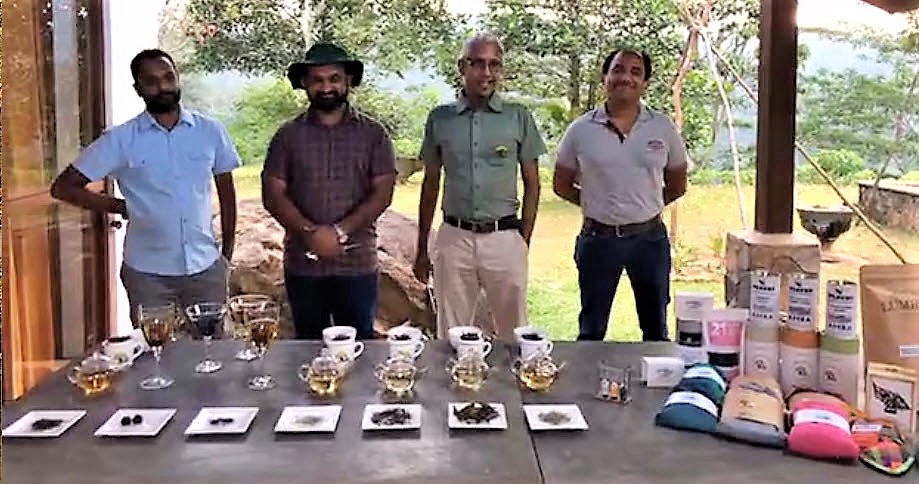
The live portion of CATA’s webinar delivered a satisfying glimpse of personality and pride a the cupping table with Kaley Tea Director Udena Wickremoesooriya and Buddika Dissanayaka, Director, Forest Hill Tea, Chaminda Jayawardana, Managing Director, Lumbini Tea Valley, and Neethanjana Senadheera, Production Manager, AMBA Estate. Each presented their best white tea, slurping and commenting. Webinar participants got a close look at the leaf and liquor along with descriptions of the tea.
When evaluating tea, considerations such as the precision of the pluck, discoloration due to oxidation, breakage, and leaf style all contribute to the buyer’s decision. Missing, of course, is the aroma, texture, mouthfeel, aftertaste, and overall organoleptic sensations. Fortunately, all this can be replicated in the buyer’s tasting room.

CATA’s webinars offer something more than samples: clues in the facial expressions, gestures, and the enthusiasm of tasters. The casual but informed banter reminded me of gaggles that formed after competitions like The Golden Leaf India Awards (TGLIA) organized by the United Planters Association of South India (UPASI) and the Tea Board of India.
These events, occasionally judged in Dubai, provided a cadre of international buyers an opportunity to discuss the results of skilled tasting judges such as Kurush Bharucha, tea expertise director and head of Unilever’s research and development, and Yahya Beyad owner of Britannia Tea.
Tasting notes with points awarded for specific characteristics motivate participants and provide bragging rights at dinner but vetting the best of the entire crop year annually also helped everyone to better understand the influence of seasonal dry spells, for example, and provided insights into the improving skills of tea makers. Artisanal innovations continuously break new ground as has been the case for centuries – but now, thanks to webinars and one-on-one tastings, innovations in tea are transmitted globally at the speed of light.
Hidden value
There is an interesting parallel in the growth of the organic tea segment that suggests public cuppings elevate the overall quality of tea. The TGLIA competition dates to 2005, a dozen years after Korakundah Tea Estate, part of the United Nilgiris Tea Estates Company, first produced organic tea.
Japan had begun labeling agricultural products in the 1950s and developed organic certifications by 1999. In 2000 JAS (Japan Agricultural Standard) adopted rules for “organic plant,” “organically grown plant,” “organic farmed,” and “organic” classifications. The United States Department of Agriculture organic program was authorized in 1990 but rules establishing the National Organic Program (NOP) were not finalized until 2002. The European Union first instituted organic rules in 1991 and by 2010 EU established an organic logo along with an indication of origin. During the past few years, all three certifications were harmonized but it will take even longer for consumers to understand the hidden value in organic.
To cash in on consumer fears about food safety and the environment marketers were quick to label certified organic products “superior” and “premium” leading consumers to pay a higher price for non-pesticide, ecologically produced teas, but evading an answer to the question: Does organic tea taste better?
Beginning in 2005 Korakundah won its first TGLIA prize. The garden won again in 2006 and for 15 consecutive years inspiring many growers to follow in their footsteps and demonstrating that organic farmed teas were equal in taste or better than conventionally grown tea.
Korakundah is part of a corporate network willing to invest in certification. Artisan tea growers recognize that third-party certifications help sell — but at a price. The webinars convey the hidden value of community building, educating youth, improving health care. Tea plantations economically purchase and maintain fleets of vehicles to bring their tea to market – Kaley chose not to buy vehicles, hiring trucks driven by villagers whenever tea needs to be transported. At Forest Hill, Buddika involves the villagers by commissioning packaging from them.
Transparency in action?
The webinars are the ideal media for demonstrating transparency. Buyers who witness the impact at origin of their purchases have more compelling visuals than labels on a tin.

Tea Biz Podcast
A survey by the American Marketing Association last year revealed US marketers increased spending on social media by 74%. During the pandemic, investment in social media grew from 13% to 23% of total marketing dollars spent, according to AMA.
Tea marketers increasingly realized that traditional strategies such as advertising and attending tradeshows, while important for branding, convert only a few leads into buyers. This is because consumer expectation has evolved over time, making personalization and customization of marketing strategies essential.
In mid-February, the Ceylon Artisanal Tea Association (CATA), a collaboration of seven Sri Lankan tea farms, hosted their third garden tour webinar. Those who attended travel virtually to see the garden processing facilities at Kaley Tea Estate attend joint live cuppings where they met the principals, and asked questions face to digital face.

Simon Bell, managing director of Amba Tea Estate and a co-founder of the Ceylon Artisanal Tea Association, writes that digital marketing is often one of the biggest challenges for small growers and rural entrepreneurs in emerging markets. In this report, Bell discusses the effectiveness of this new approach.
Tea Biz: CATA has now hosted three online webinars introducing tea producers to buyers globally. Have these webinars been effective in achieving your objectives? How so?
BELL: Absolutely, ironically, for many of the association’s founding members, finding global buyers has never really been a problem. Nearly all tea in Sri Lanka is made in large factories, so when we started producing teas by hand the products themselves were so unusual that many of the world’s best tea merchants actually tracked us down from day one before we’d even begun any marketing. We’ve always had more orders than we can handle. However, with the advent of the global lockdowns, it was apparent that we were going to lose a lot of our sales locally as the market shrunk due to the absence of visiting tourists at hotels and restaurants around the island.
And it seemed like an ideal time to bring our teams to the attention of a wider audience, and frankly, the response has been far greater than we ever expected. In normal times if you asked a tea buyer if they’d like to join a virtual tea tasting where he or she would not even get to taste the tea, I think they would very politely tell you to stop wasting their time and to send them a sample. But with everyone around the world in lockdown, including our own customers, we were amazed that the CEOs, the chief tea buyers of many of the world’s most prestigious tea merchants have been joining the webinars – and are begging us for more.
Perhaps even more important, than simply showing off our teas, what’s great about the webinar format is the ability to tell the story behind the tea. You know when it comes to artisanal teas, it’s the terroir, the climate, the provenance, the social and environmental impact that is so important to our customers in terms of why they love these teas. And so, you know, during the webinars, we walk around the estate we show the plucking, the rolling and the other steps of the process actually happening, and that’s what makes the teas so unique. These videos show you the land and the people behind the tea. And as such, they can say so much more than static images or text.
Tea Biz: Collaborating on projects like the webinar series is one example of small growers pooling resources, explain other ways that banding together benefits buyers.
BELL: I spent much of my career advising small businesses all over the world about the virtues of combining their resources and combining their efforts through associations and cooperatives and so on, not just in tea but in other areas of agriculture, in tourism, in manufacturing and so on.
Our buyers want variety, but they want that variety in terms of terroir and technique. That doesn’t mean that we can’t pool our efforts in virtually every other aspect of operations.
Joint investments in research and development in developing new varieties and planting and testing new varieties in designing new types of equipment that suit our micro-scale teas. In commissioning equipment from engineering companies which wouldn’t be interested if we were just commissioning on our own from joint purchasing of packaging and certification services and other types of inputs like that that would typically only be affordable to larger enterprises. All across the chain, including, you know, making our voice heard with the government we are much better working together than we are separately. And perhaps most importantly, from a buyer’s perspective, we offer the opportunity to pool their purchases and their shipping, lowering costs. Two or three of our members are already working together and jointly shipping product to several customers around the world saving the customers time and money that they otherwise would be spending having to coordinate orders and shipments from multiple suppliers while giving them the variety that their consumers demand.
Ultimately, we hope to be able to offer buyers a one-stop shop where they can order a whole menu of different Ceylon artisanal teas representing all the different varieties in all the different growing regions of Sri Lanka.
Do webinars work?
The novelty of webinars waned from a time when 73% of B2B marketers and sales leaders identified webinars “as the best way to generate high-quality leads” yet 76% of B2B buyers used webinars in 2019. Last year the number of webinars soared, accelerated by the pandemic. Businesses all over the world are using webinars to attract customers, promote products, and build loyalty.
The Big Book of Webinar Stats, published in 2019, found that webinars were most commonly used by software, financial services, and consulting firms. Since that time travel and tourism, real estate, and retail use have increased. Health care webinars surged in the past year. Agriculture has lagged but travel restrictions, the additional costs, and the inconvenience of flying make webinars an ideal opportunity for small tea ventures to inform and attract buyers.
Go To Webinars analyzed 250,000 webinars to offer these tips.
The most effective channel to promote webinars is email. Expect 59% to register the week leading up to the event with 17% registering same day.
- Thursday is the best day to schedule.
- Mornings 9-11 am are the best hours for attendance
- 84% of attendees prefer webinar replays (vs live)
- 66% of webinars attract 50 or fewer attendees
- Attendee engagement drops off at 57 minutes. The ideal length is 45-60 minutes but attendees will stay for about 70% of a webinar that lasts up to 90 minutes.
Link to share this post with your colleagues
Subscribe to the Tea Biz newsletter and view archive
Subscribe and receive Tea Biz weekly in your inbox.

