Hear the Headlines
| Tea History Collection Unveiled
| Indian Commodities Logjam
| THIRST Undertakes a Tea Human Rights Analysis
| A Series of Major Quakes Rattle Yunnan

Features
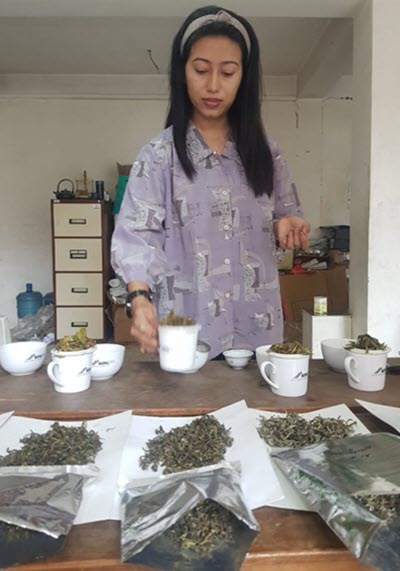
Tea Biz this week travels to Nepal to meet Aasha Bhandari the newly named International Trade and Promotion Executive at the Himalayan Tea Producers Cooperative
…and to the North Carolina campus of Wake Forest University to learn from student William Liu why ancient teas and rituals retain their appeal with young people.

Himalaya Tea Opportunity
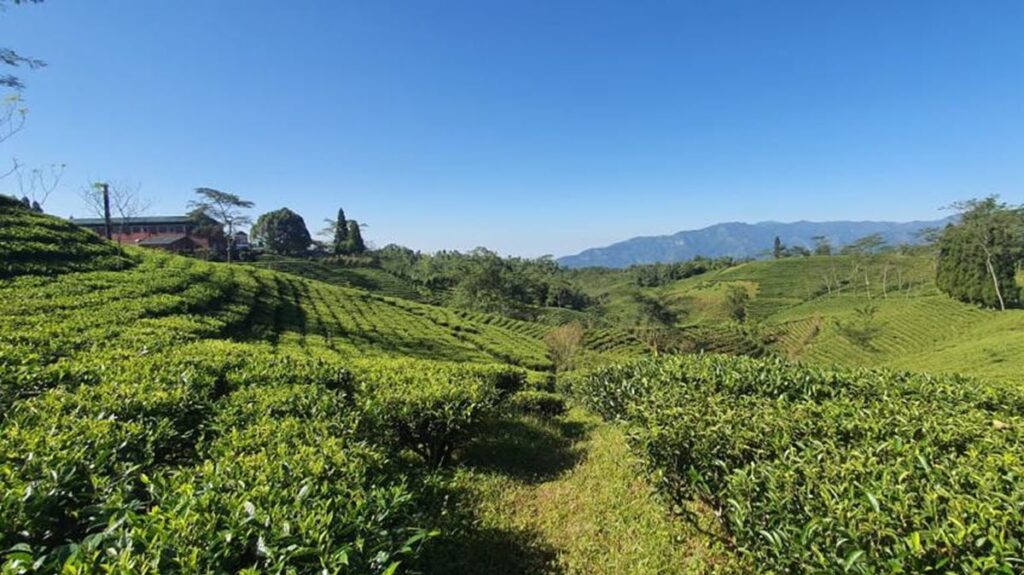
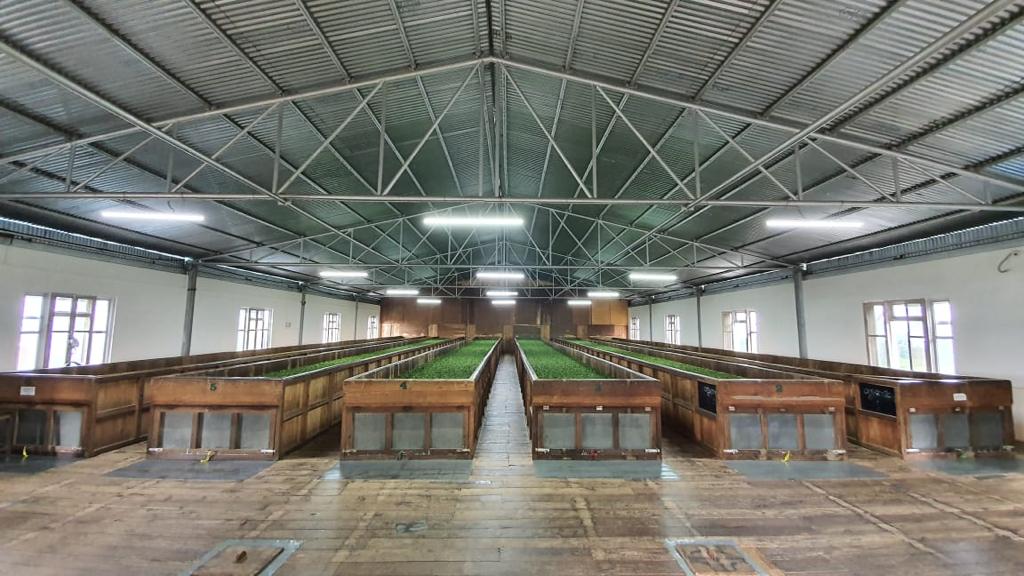
Nepal Increases Production of Quality Specialty Teas
By Aravinda Anantharaman | Bengaluru
Nepal’s tea industry reported record sales in 2020. The fabled tea land is growing greater quantities and greater varieties of loose and broken leaf teas thanks to a government-initiated expansion of the industry to high altitude gardens in non-traditional growing areas. Rural agrarian entrepreneurs are redefining offerings for an international market thirsty for the distinct taste of Himalayan grown oolongs, white teas, and premium black whole leaf. In this segment Aasha Bhandari, newly named to promote trade at the Himalayan Tea Producers Cooperative, discusses her plans for HIMCOOP.

Why Ancient Tea Appeals to Young People
By Dan Bolton
William Liu is a 20-year-old sophomore at Wake Forest University so inspired by tea that he and his classmates established the World Tea Association on campus and online. The group offers tea discovery and tasting sessions weekly and hosts occasional tea panels with presentations by tea professionals, tea scholars, and tea explorers. The events bring together many who are new to tea, says William “we aim to redefine the tea experience through an interdisciplinary approach and expose the true leaf to a greater audience.”
In this discussion he describes why tea appeals to young people and explains his view that tea learning is ongoing. “The tea journey has no destination, he says, it involves only intention and lifelong learning.”
Tea News you Need to Know
By Dan Bolton
An extensive private collection of historical tea artifacts and modern facilities for meetings and tea research were unveiled on International Tea Day by Tea Ambassador Mike Bunston, OBE.
The Tea History Collection, located in Banbury, Oxfordshire in the DCS Group complex, is the inspired work of entrepreneur Denys Shortt, OBE (Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire). The facility, valued at £100,000 ($140,000) is open by appointment to tea-related organizations and academia. It is equipped with a tasting bar, high-speed internet, archive cabinets, a video-conference room and work areas.
Shortt, who founded DCS in 1994, grew up on a tea estate in Assam. His family worked at gardens there for 20 years before moving to Africa where his father managed the Ikumbi Tea Factory in Thika, Kenya.
“We do not believe there is anything like this in the world,” says Shortt. “We have items from Plantation House (now demolished) which was where the London Tea Auctions were held.” The collection of more than 500 items includes teas, books, and sample cabinet with 200 tins containing teas dating to 1904. The collection will be maintained as a non-profit.
Commodities Logjam
Fifty thousand in West Bengal are homeless this week due to a tropical cyclone that halted air traffic and port activity in Calcutta. Every link of India’s tea supply chain is under stress. Restrictions to stop the spread of COVID-19 are once again limiting the number of harvest workers in the gardens and reducing by half staffing at factories processing tea, while simultaneously forcing the cancellation of tea auctions… delaying transport and causing local warehouses to overflow.
Truckers essential to transporting tea were virtually halted last year and while many delivering to cities face delays due to curfews that prevent unloading at night, local transport is much less problematic in 2021.
The weak link in the commodities supply chain during the second wave are buyers who cannot easily judge what quantities are required for manufacturers and to meet varying retail demand. For example, Kochi-based spices trader Kishor Shamji told the Hindu Businessline that a lack of buying interest from masala manufacturers in upcountry markets has affected the sales of almost all spices, including pepper, cardamom, ginger, nutmeg, and cloves. Meanwhile, traders worry that the tea they purchase to send overseas will experience costly shipping fees and delays. Last year’s first wave dealt urban areas the hardest blow but in 2021 it is rural areas that suffer.
Biz Insight – In India, as in many countries, mandatory lockdowns and health concerns have accelerated sales of tea. A survey of 22,000 rural small market stores known collectively as Kirana revealed a 140% increase in tea sales. Sales of hand sanitizers that appeared near the top of the list last year are flat but sales of soap increased by 50%, according to StoreKing. Pest and mosquito repellent experienced a 200% increase and comfort snacks and biscuits are up 83%.
Assessing Human Rights in Tea
THIRST The International Round Table for Sustainable Tea, is launching a three-year program to analyze the root causes of human rights breaches in the tea industry and come up with an action plan for how to solve them.
Founder Sabita Banerji objects to “rights assessments” which have a negative connotation she favors an “impact analysis.” Banerji calls it a ‘constructive solution-oriented approach’.
The program will document conditions for workers and farmers and identify problems “but more importantly, what can be done to address these problems,” said Banerji. The first step is to consolidate existing research and then conduct in-depth studies where there are gaps, providing a global picture of the interdependencies of tea.
Read more on the Tea Biz blog.
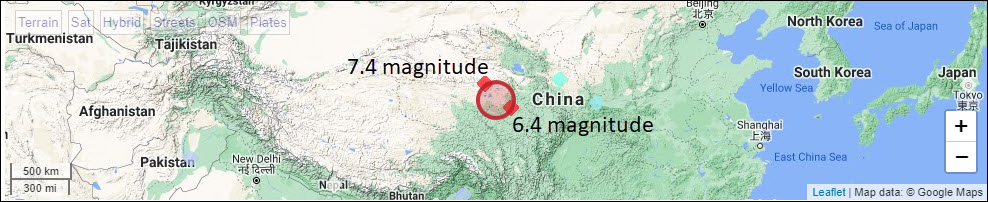
A Series of Major Quakes Rattle Yunnan
Three major earthquakes and hundreds of aftershocks damaged 14,000 structures, killed three people and seriously injured 28 in Yunnan Province last week. The first in the series struck Dali located near the heart of the tea growing region. That deadly 6.0 magnitude quake on Tuesday was followed Friday by a much stronger 6.4 quake that damaged homes and forced rescuers to pull several people from under debris. Five hours later a 7.4 temblor located in adjacent Yangbi [YANg BY] rattled Yunnan again.
The steep mountainous region, subject to landslides, is jittery about quakes. In 2008 a 7.9 earthquake centered in Sichuan province killed 87,000 people and left 4.2 million homeless, causing $150 billion in damage.
Share this episode with your colleagues
https://teabiz.sounder.fm/episode/news-01212021
Subtext
Avoid the chaos of social media and start a conversation that matters. Subtext’s message-based platform lets you privately ask meaningful questions of the tea experts, academics and Tea Biz journalists reporting from the tea lands. You see their responses via SMS texts which are sent direct to your phone. Visit our website and subscribe to Subtext to instantly connect with the most connected people in tea.
Subscribe and receive Tea Biz weekly in your inbox.